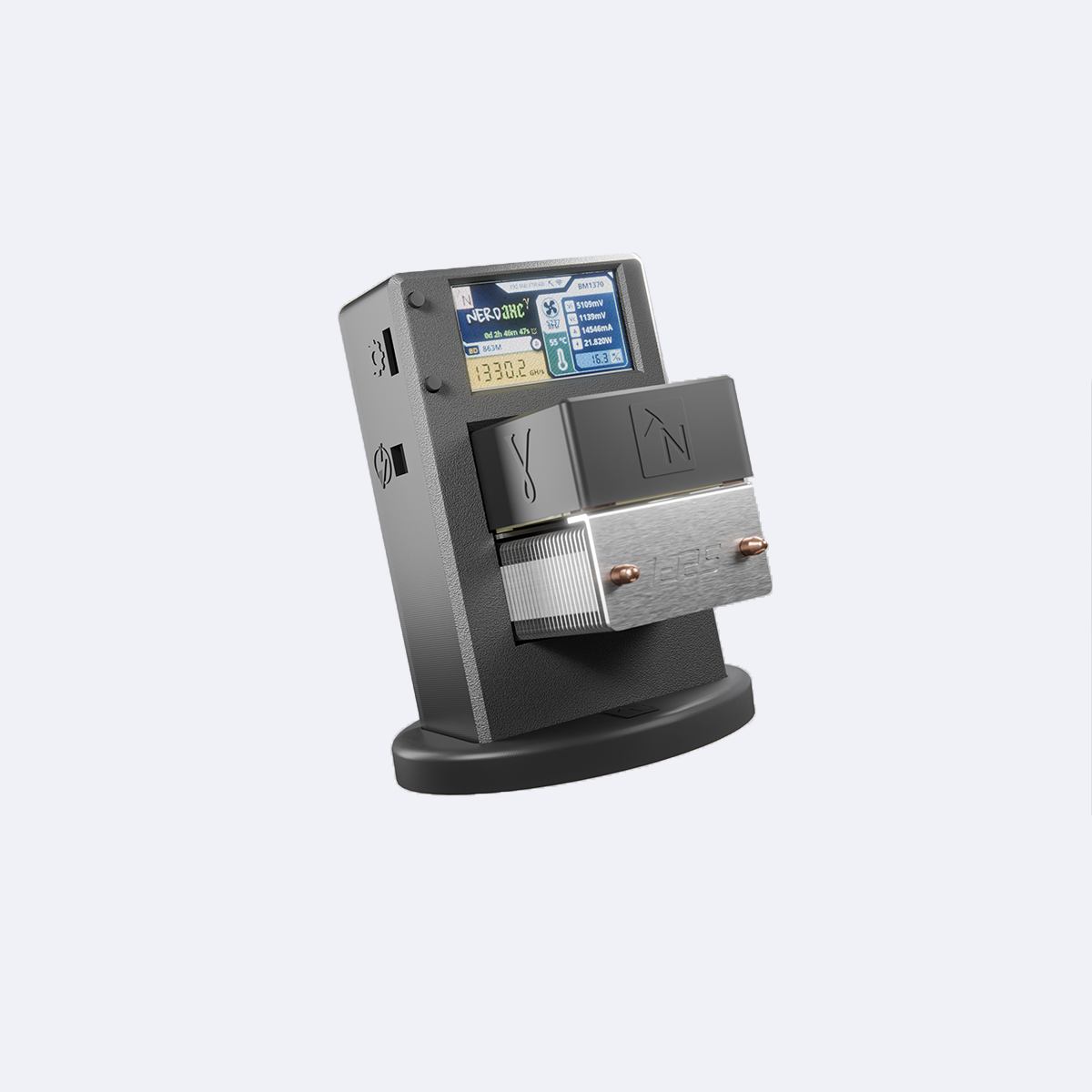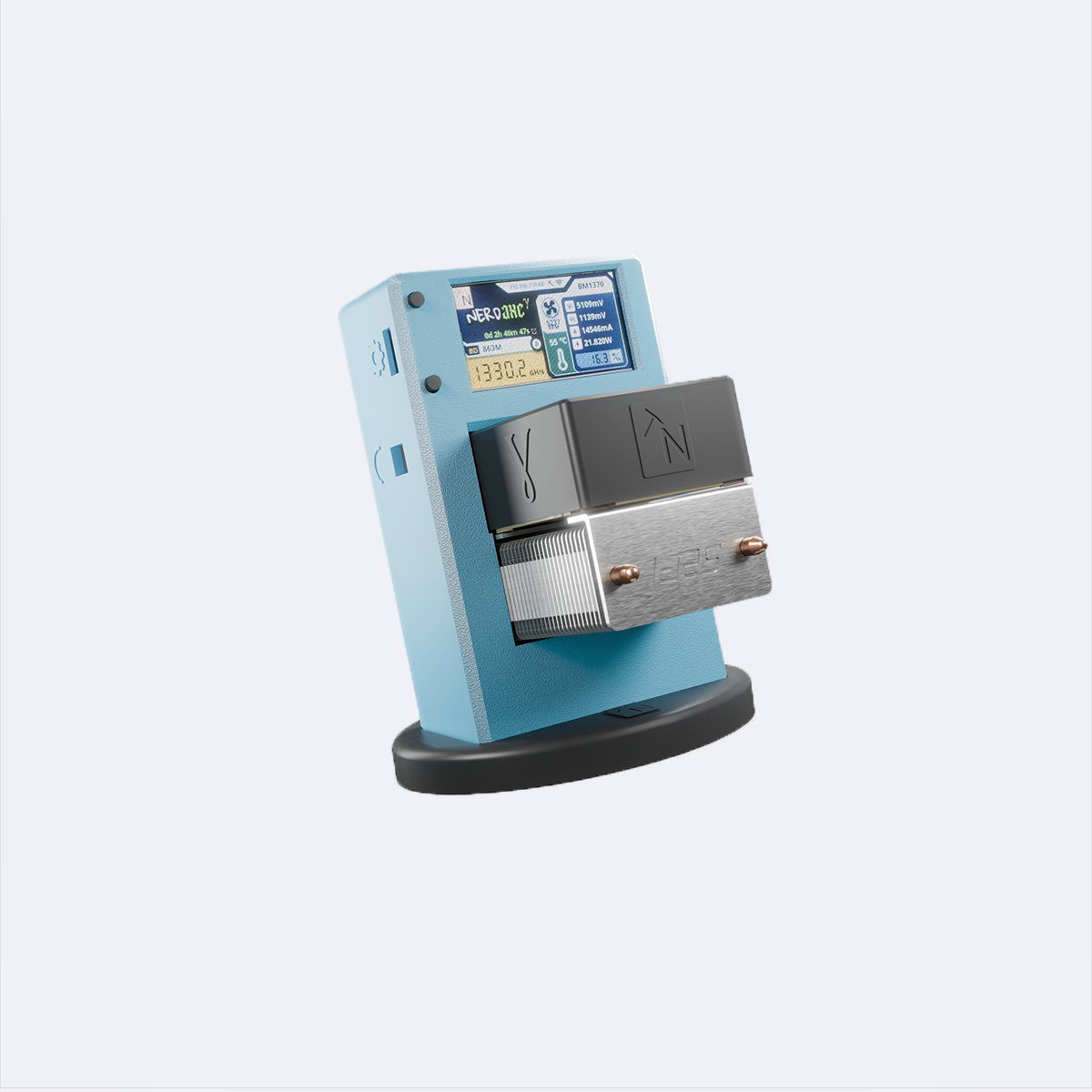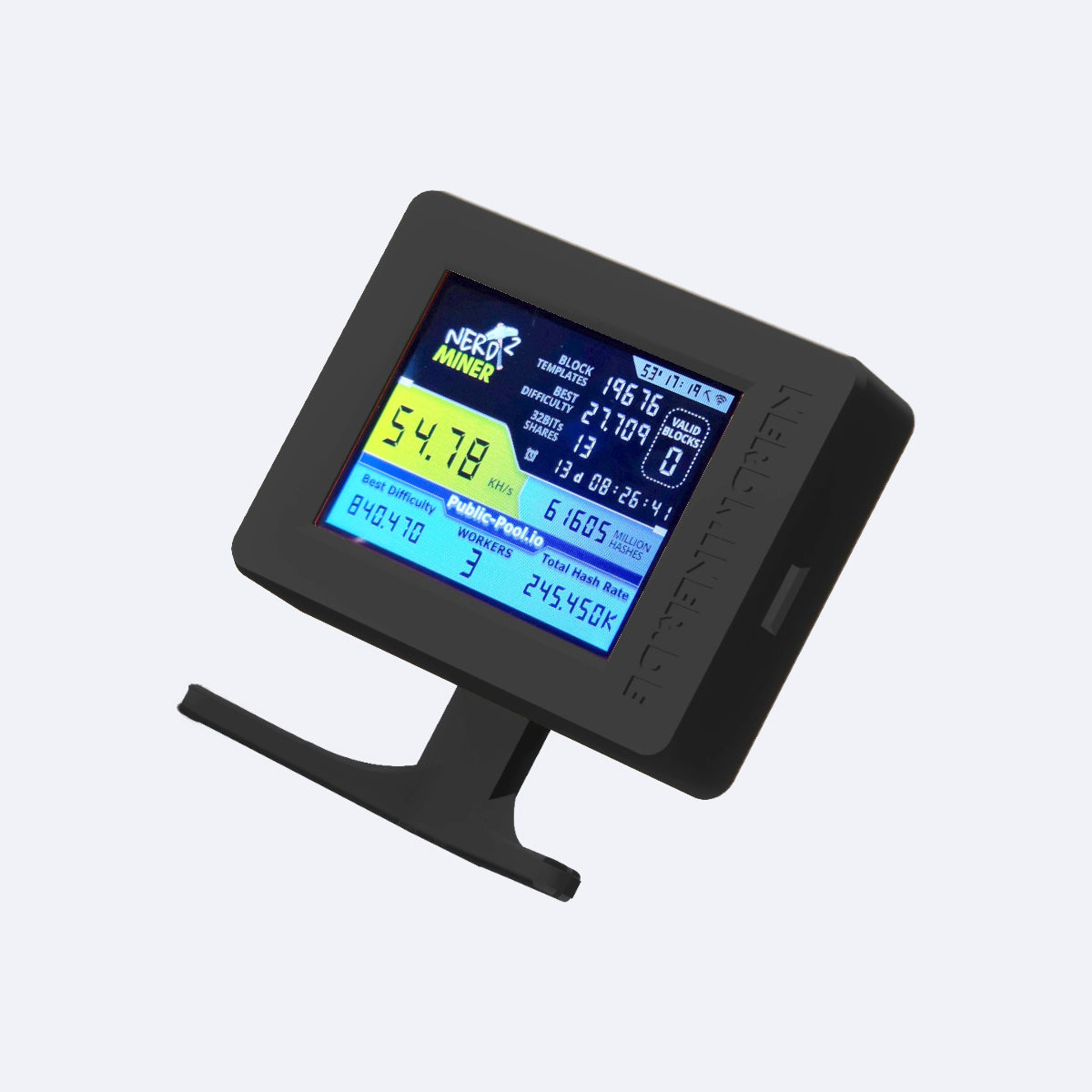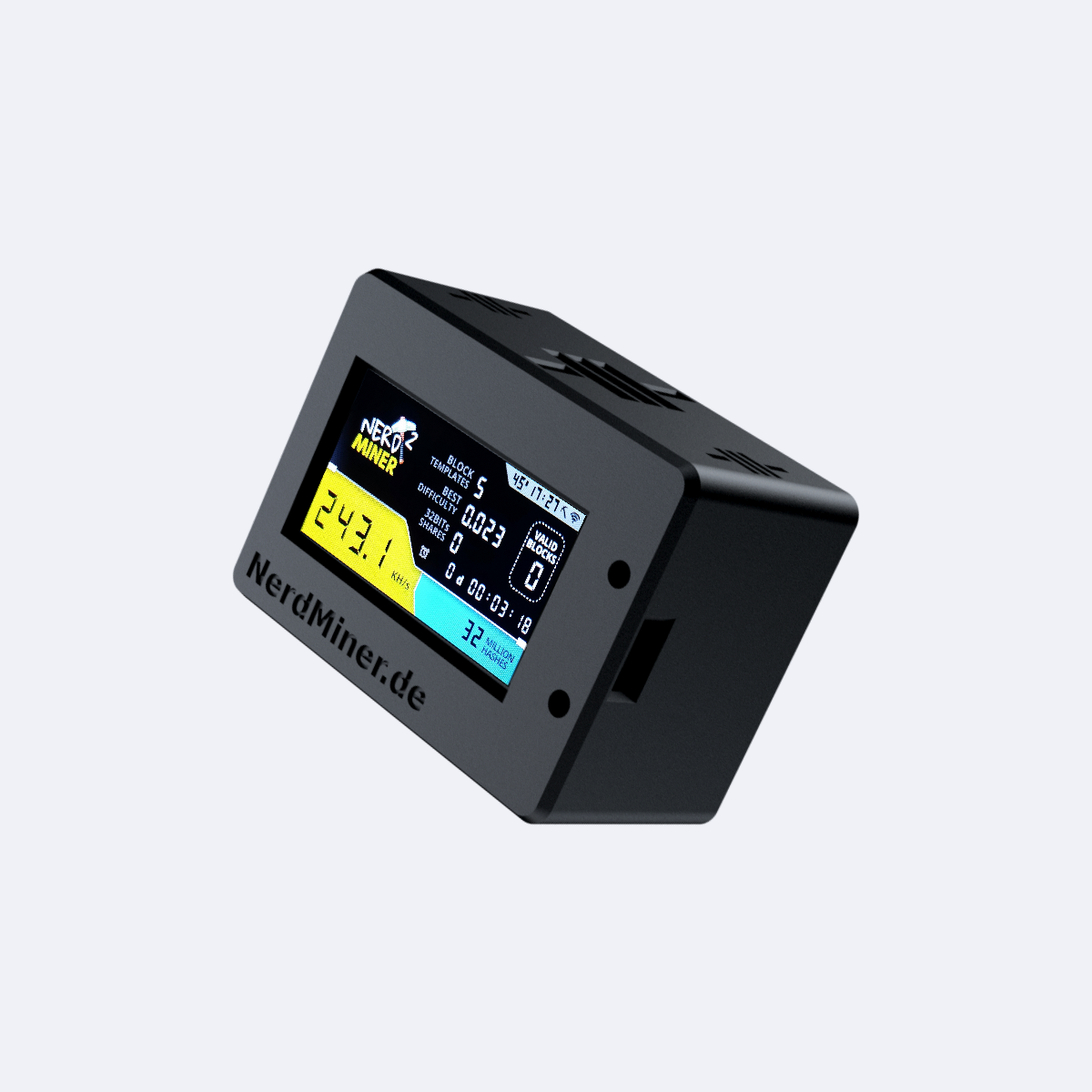
Der perfekte Einstieg in die Bitcoin Welt
Trusted by Creators

Die Fullnode – Der Guardian deiner finanziellen Souveränität
Mit der neuen Metal Edition setzt du ein Statement: maximale Sicherheit, maximale Langlebigkeit, maximal deine.

Deine Superkraft: Mining
Nerdminer.de ist mehr als Technik – es ist der Ausdruck deiner digitalen Unabhängigkeit. Erlebe Bitcoin-Mining als Abenteuer, nicht als Anleitung.
Blog posts
The 20 most important terms in Bitcoin
Bitcoin is on everyone's lips, but getting started can be confusing with a variety of technical terms. Here are the 20 most important terms that beginners should know: 1. Blockchain: A decentralized and distributed database that stores transactions securely and transparently. 2. Cryptocurrency: A digital or virtual currency that uses cryptographic techniques for its security. 3. Bitcoin: The first and most famous cryptocurrency, introduced by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2009. Also the only decentralized cryptocurrency. 4. Altcoin: Any cryptocurrency other than Bitcoin, such as Ethereum, Ripple and Litecoin. Altcoins represent centralized or distributed networks, which, however, do not fulfill the aspect of decentralization, as a central entity always manages the network. 5. Bitcoin Wallet: A digital wallet that allows storing, sending and receiving Bitcoin. 6. Bitcoin Mining: The process in which, on the one hand, the Bitcoin network is secured and, on the other hand, new Bitcoin are created by applying energy. 7. Hash: A cryptographic function that converts data into a specified string and is used to secure information on the blockchain. 8. Smart Contracts: Self-executing contracts based on the blockchain that are automatically executed when certain conditions are met. 9. ICO (Initial Coin Offering): A financing method in which new cryptocurrencies are introduced by selling tokens to investors. 10. Fork: The fork of an existing blockchain that leads to a new version, such as hard forks and soft forks (example Bitcoin Cash) 11. Private Key: A secret key that allows one to access their cryptocurrencies and authorize transactions. 12. Public Key: A public key that allows others to send cryptocurrencies to a specific wallet. 13. Exchange: A platform where cryptocurrencies can be bought, sold or exchanged. 14. All-time high: All-time high of the price of a cryptocurrency in fiat currencies. 15. Stacking Sats: Regular saving in Bitcoin, e.g. in the form of a weekly or monthly savings plan. 16. Bitcoin Whale: An individual or group that owns a significant amount of Bitcoin and can thereby exert an influence on the price. 17. FOMO (Fear of Missing Out): The fear of missing out on a lucrative opportunity, which often leads to impulsive investment decisions. 18. Market Cap: The total value of all units of a cryptocurrency in circulation. 19. Fiat currencies: The current government-run inflationary currencies such as the dollar or euro. 20. Hardware wallet: A wallet that is not connected to the Internet and is therefore protected from hacker attacks (e.g. the Bitbox). With these basic concepts you will be better equipped to dive into the fascinating world of Bitcoin. Become a Bitcoin miner now
Learn moreAn introduction to Bitcoin mining: How does it work and why is it important?
How does Bitcoin mining work?1. Collect transactions: First, the network collects unconfirmed transactions in a so-called "mempool". When a user sends a transaction, the transaction ends up in this mempool. It is comparable to a queue.2. Formation of blocks: Miners select transactions from the mempool and group them into a block. For economic reasons, they always select the transactions that generate the most fees.3. Reward for miners: Miners are rewarded for their energy expenditure with new Bitcoin. This is the mechanism that brings new Bitcoin into circulation. From 2009 to 2012 it was 50 Bitcoin per block, 2012-2016 25 Bitcoin, 2016-2020 12.5 Bitcoin, 2020-2024 6.25 Bitcoin and since the halving in April 2024 only 3.125 Bitcoin. This represents Bitcoin's monetary inflation, which was around 1.6% before the halving in 2024 and has halved to 0.8% since the halving, meaning that inflation is now lower than it is for gold.Challenges and future prospectsBitcoin miners are faced with the dilemma that halving reduces their turnover by 50% every four years. This indirectly forces miners to constantly reduce their costs as much as possible in order to achieve maximum efficiency.The biggest items are electricity consumption and hardware costs. Halving every four years means that miners are always on the lookout for cheaper electricity, which can primarily be found in unpopulated areas of the world through surplus energy, i.e. electricity that would otherwise not be purchased by anyone. ConclusionBitcoin mining is a fascinating process that ensures the integrity of Bitcoin.Discover your Nerdminer
Learn moreThe Lightning Network: The Future of Bitcoin Transactions
Bitcoin was released in 2009. Since then, the community of people interested in Bitcoin has continued to grow. However, there have also been criticisms of Bitcoin since its inception, such as the lack of scaling options, potentially expensive fees on the main network and the lack of privacy in payments. The so-called Lightning network was ultimately created to address these problems. The Lightning Network was first proposed and developed in 2015. However, there were different stages of development. The implementation and introduction took place gradually over the years. What is the Lightning Network? The Lightning Network is a so-called "second layer" or "off-chain" solution for the Bitcoin network, which was created, among other things, due to the blockchain trilemma. Blockchain trilemma The blockchain trilemma describes the fact that a distributed database, such as Bitcoin, can only maximize two of the three properties of security, decentralization or scalability. It is considered impossible for a blockchain to be decentralized and secure and still be extremely scalable. If a blockchain attempts to scale by increasing the size of the blocks in the blockchain, the costs of operating a so-called fullnode (a computer that stores the entire blockchain and validates the transactions) increase. The larger the blocks in a blockchain, the greater the bandwidth, processing and storage requirements for each individual full node. Increasing the transaction capacity and the associated increase in the size of the blocks would have the undesirable effect of centralizing the system, as only large companies and no private individuals could afford to operate a full node. Blockchain and Lightning easy to understand Imagine the Bitcoin network as a classroom filled with students. If you want to send a classmate a Bitcoin, you both stand up, tell all the other students that you want to make this transaction, and all the other students will write this transaction down in their notebooks. This is therefore not only time-consuming, but also expensive and is not really anonymous. If you want to use the Lightning Network, think of it as telling all students that you and your classmate will be leaving the classroom. All students write down how many Bitcoin you and your classmate leave the classroom with. Outside of the classroom, you can now send transactions to your classmate and back billions of times per second, without any fee, without anyone knowing. When you decide that you no longer want to transact with your classmate, you both come back to the classroom and tell all students how many Bitcoin you each have left. Now all students write this down again. How does the Lightning Network work technically? At its core, the Lightning Network enables transactions to be carried out outside of the blockchain. This is done by opening a so-called “payment channel” between the parties involved. Instead of writing every single Bitcoin transfer to the blockchain, users can make a series of transactions directly between themselves and share the transaction data with each other. Only when the payment channel is closed is the final transaction data written to the blockchain. Advantages of the Lightning Network: 1. Speed : Transactions on the Lightning Network are implemented almost instantly, in contrast to the slower transaction times on the Bitcoin blockchain. 2. Cost efficiency: Since transactions are carried out outside the blockchain and no proof of work in the form of mining is required, fees are significantly lower in the cent range. 3. Scalability: The Lightning Network allows Bitcoin to process a much larger number of transactions without overloading the blockchain. Technically, Lightning does not have a maximum number of transactions that can be made per second. 4. Micro-transactions: The Lightning Network opens up new possibilities for micro-transactions, as transactions can theoretically be carried out in cents and every second. An example is streaming for Bitcoin podcasts, which are billed in Satoshis per second. 5. Privacy: Since transactions occur off-blockchain within private payment channels, they are private and are not publicly recorded. How to use the Lightning Network? To use the Lightning network, you need a Lightning-enabled Bitcoin wallet such as the Wallet of Satoshi or the Phoenix Wallet, which can be downloaded from the Android or Apple store. These wallets support sending and receiving payments via the Lightning Network. Once you have such a wallet, you can send and receive payments to other Lightning users. Is it already used a lot? The use of the Lightning Network has become increasingly widespread in recent years. Especially in countries where people are suffering more from the current monetary system, they are looking for alternative payment methods. One example is the people from El Salvador, many of whom work in the USA and whose remittances back home make up a large part of El Salvador's gross domestic product. Until now, these people had to rely on expensive channels such as Western Union, whereby the transactions not only sometimes included 20% fees, but also took several days. With Lightning, these people now have almost no fees when sending the money they have earned, are not dependent on a third party like Western Union and can send money to their home country peer-to-peer within a second. Challenges and future prospects: Although the Lightning Network is promising, there are still some challenges ahead. These include the ease of use of wallets, the reliability of payments and acceptance by the general public. Nevertheless, developers around the world are continually working on improvements to make the Lightning Network even more robust and beginner-friendly. Conclusion: The Lightning Network is an exciting development that has the potential to make Bitcoin an even more useful and versatile means of payment. Through its ability to make transactions fast, inexpensive and scalable, the Lightning Network could make a major contribution to the further adoption of Bitcoin as money. Discover the Bitcoin miner for your desk
Learn moreBitcoin-Wallets: What you should definitely know
Bitcoin wallets are essential tools for the secure storage and management of Bitcoin. There are different types of wallets, each of which has different advantages and disadvantages.The most important types of Bitcoin wallets and their features are described in detail below.1. Software wallets:Software wallets are programs that are installed on a computer or mobile device. They come in various forms: Desktop wallets, mobile wallets and web wallets.-> Desktop walletsDesktop wallets are installed on a PC or laptop and offer users full control over their Bitcoin. Advantages: - Ease of use: they offer a user-friendly interface and various functions for managing Bitcoin. Disadvantages: - Vulnerability to malware: If the computer becomesinfected with malware, the Bitcoin can be stolen. The Bitcoin is only as secure as the computer is.- Device dependency: If the device is lost ordamage to the device, access to the Bitcointo the Bitcoin can be lost unless backups have been created.-> Mobile walletsMobile wallets are apps that are installed on smartphones and allow users to manageusers to manage Bitcoin on the go. Advantages: - Portability: You can manage Bitcoin anywhere and at any time.- User-friendliness: Often designed to be very user-friendly. Disadvantages: - Security risks: Smartphones are vulnerable to hacking andvulnerable to hacking and malware due to the internet connection.- Risk of loss: If the cell phone is lost or stolen, the Bitcoin could also belost if no security measures such as backup and encryption have been taken.-> Web walletsWeb wallets are online services that enable access to Bitcoin via a web browser. Advantages: - accessibility: you can access theBitcoin from anywhere as long as there is an internet connection.- Easy to set up: No download or installation required. Disadvantages: - Low security: as the private keys are stored on the provider's servers, there is an increased risk of hacking and fraud.- Dependence on the provider: In the event of a service failure or fraudulentfraudulent activities of the provider, the Bitcoin can be lost.2. Hardware walletsHardware wallets are physical devices that have been specially developed for the secure storage of Bitcoin. They store the private keys offline. Advantages: - High security: As the private keys never come into contact with the Internet, they are protected against online attacks. The security of hardware wallets lies in their architecture. As they work offline thanks to a special secure element, i.e. they are not connected to the Internet, hackers cannot gain direct access to the private keys. Even if a usertransactions, the signature process is carried out offline on the device and only the signedand only the signed transaction is transmitted online. This“cold storage” method significantly minimizes the risk of theft through online attacks.- Protection against malware: Even if the computer is infected with malware, the private keys remain secure.- Ease of use: Many hardware wallets offer a user-friendly interface and simple transaction processing. Disadvantages: - Cost: Hardware wallets are significantly more expensive compared to software wallets.- Complexity for beginners: The initial setup can be a little more complicated for beginnerscomplicated for beginners, as they have to make a note of the Bitcoin seed offline.offline.3. Paper walletsA paper wallet is a physical copy or printout of the private and public keys of a Bitcoin address. Advantages: - High security: As it is a physical document, there is no digital point of attack when it is used.- Free of charge: There are no costs for thecreation of a paper wallet. Disadvantages: - Risk of loss: If the paper is lost or damaged, the Bitcoin cannot be recovered.- Cumbersome to use: Transferring Bitcoin to a paper wallet or spending Bitcoin requires additional steps and can be complicated for beginners.- No flexibility: It is more difficult to spend Bitcoin from a paper wallet as this requires importing the keys into a software wallet.- Dependence on the production provider: Generating the paper wallet requires trust in the provider that offers the production of paper wallets.Experience from the Bitcoin space:Most people in the Bitcoin space use cell phone wallets for everyday payments. The Wallet of Satoshi is recommended for beginners and the Phoenix Wallet for advanced users. Bitcoiners hold roughly the same amount of Bitcoin there as they do in cash in their wallets. Almost all Bitcoiners use a hardware wallet for their savings. The Bitcoin Only version of Bitbox is particularly recommended, as it has certain advantages over other hardware wallets. Paper wallets can be used for gifts to relatives, where, for example, €50 in Bitcoin can be given as a gift.Conclusion:Each type of Bitcoin wallet has its own advantages and disadvantages. The choice depends on the individual needs andsecurity requirements. While software wallets are practical anduser-friendly, hardware wallets offer the highest level of security by storing the private keys offline. Paper wallets can also be a secure option, but require careful handling and storage. Get your BitBox for maximum security
Learn more









































